June 9, 2020 – Data extracted and analyzed by Atlas VPN reveals, the amounts of demanded ransom payments increased by 140 percent, comparing the numbers of 2018 to 2019. More and more organizations succumb to blackmail: 57 percent of organizations settled and paid the ransom during the last 12 months.
Ransomware is a type of malicious attack where a criminal encrypts, typically, sensitive files, then threatens to publish them, unless a demanded ransom is paid.
The team of Atlas VPN researchers added the average sums hackers were demanding during each quarter in 2018 and 2019 globally, then divided the number into four.
The Average Ransomware Sum in U.S. Dollars
In 2018, the requested ransom payments reached 7.6 thousand dollars on average, globally. During the first quarter, the monetary amount of requested ransom payments hit $5,400 on average, Crypsis report suggests.
The number increased to $8,300 amid the second quarter and peaked in the third quarter, reaching $10,000 on average. During the fourth quarter, criminals were requesting companies to pay $7,000 on average.
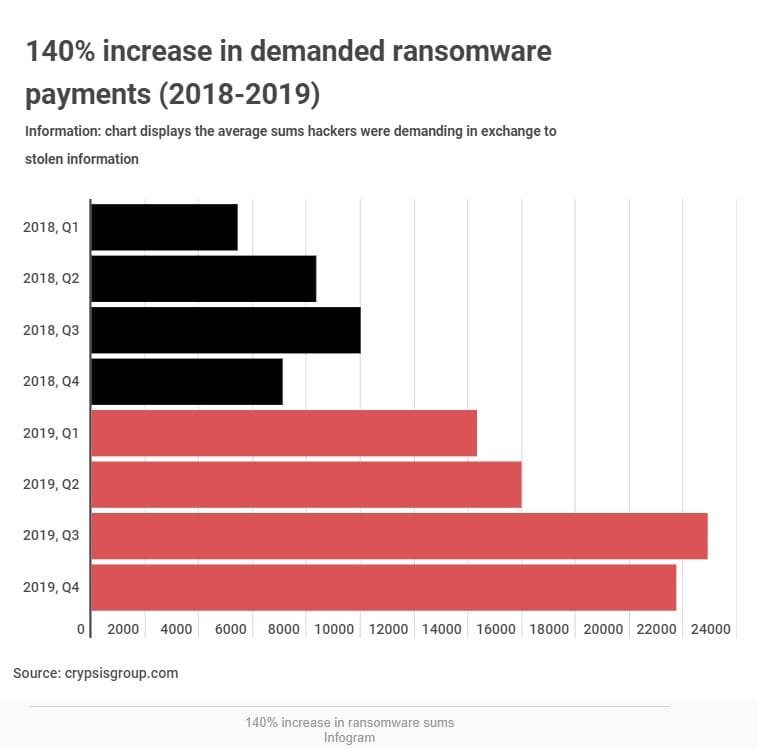 It is safe to say cybercriminals got more greedy in 2019: by encrypting companies’ files, they were requesting $18,000 on average. The number is 140 percent bigger in comparison to 2018.
It is safe to say cybercriminals got more greedy in 2019: by encrypting companies’ files, they were requesting $18,000 on average. The number is 140 percent bigger in comparison to 2018.
The average number spiked dramatically amid the first quarter, hitting $14,000 and continuing to increase. In the second quarter, it spiked to nearly $16,000 on average.
The sum peaked in the third quarter of 2019, hitting $22,800 and being the largest demanded amount during the two-year period. It then dropped to $21,700 amid the last quarter of 2019.
Majority of Companies Settle and Pay the Ransom
More and more companies disclose a ransomware attack has victimized them. In 2018, 55 percent of companies admitted they received a request to pay ransom during the last 12 months globally. The number increased to 56 percent in 2018 and jumped to 62 percent in 2020, a CyberEdge report suggests.
The percentage of companies that agreed to pay the ransom has been on the rise, too. Thirty-eight percent of victimized companies paid the demanded sum in 2018, and 45 percent in 2019. In this year’s survey, even 57 percent of organizations paid a ransom to have their data recovered during the last 12 months.
Unfortunately, paying the ransom does not necessarily get you the stolen information back. In 2018, 49 percent of organizations that paid ransom were able to recover their data. In 2019, the number increased to 61 percent and jumped to 66 percent in 2020.
Leading Ransomware Causes
However, the fact that companies were able to recover the stolen information does not suggest paying the ransom. Instead, companies should be focusing on preventative methods to ensure these attacks do not happen at all. Not only is your information at risk of being lost, but these incidents also disrupt the business processes.
To avoid ransomware attacks, it is vital to study the leading reasons behind these incidents. Surveys Atlas VPN analyzed reveal that leading causes can be divided into two categories: outside and inside threats.
CyberEdge conducted a survey asking business experts to rate how likely certain events are to lead to a cyber incident. Concern for suffering from a ransomware attack due to poorly trained staff was the highest, reaching a 72 percent rate.
Also, respondents rated low security awareness (72 percent) as the second most common reason behind cyber incidents. Concern for not being able to ensure smooth threat detection and response processes reached a 70 percent rate.
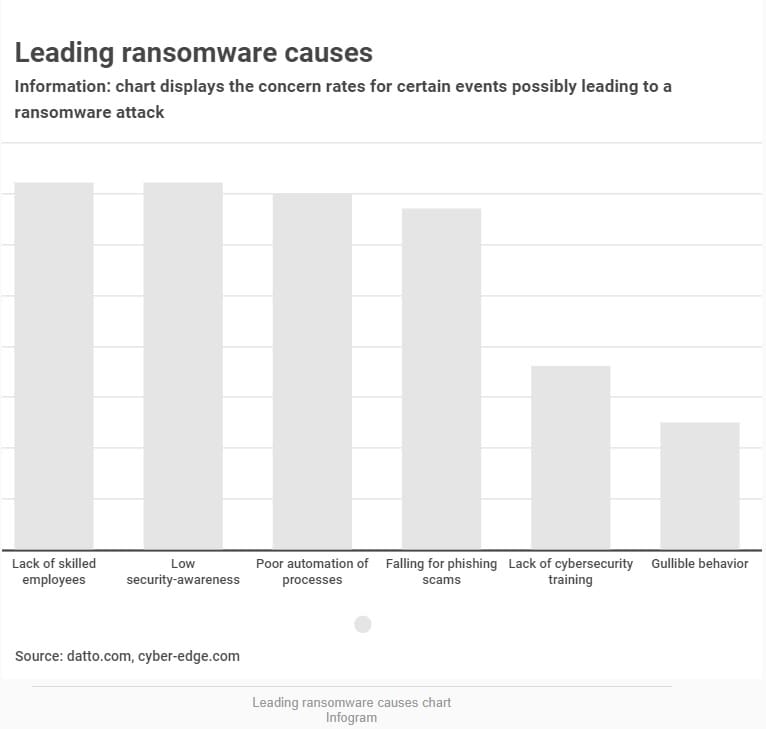 While the survey conducted by CyberEdge focuses on the inside issues businesses should sort out, Datto research analyzes the outside threats. Sixty-seven percent of 1,400 respondents consider falling for phishing scams to be the most common cause of ransomware infections.
While the survey conducted by CyberEdge focuses on the inside issues businesses should sort out, Datto research analyzes the outside threats. Sixty-seven percent of 1,400 respondents consider falling for phishing scams to be the most common cause of ransomware infections.
The second reason is the lack of proper cybersecurity training with a 36 percent concern rate. Finally, 25 percent of respondents agreed that people being naive and gullible is associated with ransomware incidents.