Financial institutions worldwide face a complex transition as payment systems migrate to ISO20022 standards with staggered deadlines through November 2025. Kevin Lee of Cygnus Compliance maps the implementation timeline across CHIPS, FED and SWIFT networks, revealing how expanded data fields and text-based message tags demand systematic remapping of compliance frameworks to prevent monitoring gaps and false positives.
The global payments ecosystem is undergoing a significant transformation with the adoption of ISO20022, a new standard that fundamentally changes how financial institutions process and monitor transactions. This shift presents both opportunities and challenges for compliance professionals.
ISO20022 replaces traditional payment message formats with extensible markup language (XML), offering greater flexibility and the ability to handle complex data structures. This allows financial institutions to integrate additional transaction details within a single message and addresses industry challenges with parsing free text fields.
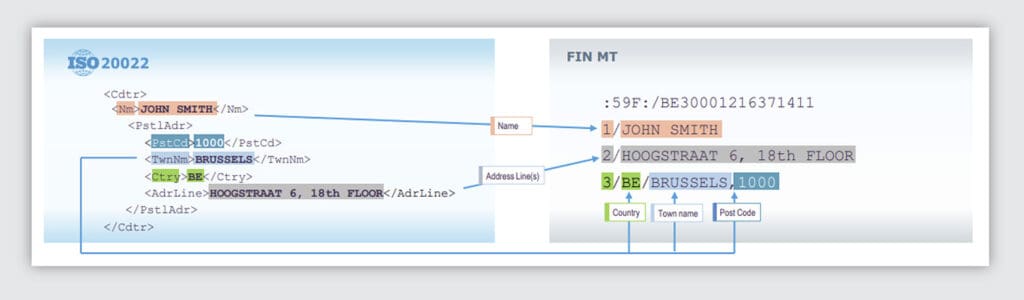
For example, the dedicated country code field in the ISO20022 format enables financial institutions to easily extract this critical data element for transaction monitoring, sanctions screening and other regulatory compliance controls. Before ISO20022, there was no effective, scalable way to reliably mine country code data from free text.
Another benefit: The new structure allows for long addresses to be fully captured without data loss by design.
Implementation timeline
Financial institutions must adhere to specific deadlines for ISO20022 implementation across different payment systems:
| Payment type | Deadline |
| CHIPS | April 2024 |
| FED | July 2025 |
| SWIFT | November 2025 |
| ACH | To be announced |
- The Clearing House (TCH) completed its CHIPS ISO20022 implementation in April 2024.
- The Federal Reserve will adopt the ISO20022 message format for the Fedwire Funds Service in a single-day implementation July 14, 2025, sunsetting the existing proprietary Fedwire Application Interface Manual (FAIM) format.
- SWIFT confirmed November 2025 as the end of the MT/ISO20022 cross-border coexistence period, with priority given to payment instruction messages.
- While NACHA (National Automated Clearing House Association) has developed an ISO20022 mapping guide for ACH transition, no conversion deadline has been announced.
Investment Advisers Begin Critical Year of AML Compliance Planning
FinCEN signals broad interpretation of suspicious activity as advisers prepare for compliance
Read moreDetailsMessage types and data elements
ISO20022 introduces three broad categories of message types:
- pacs: Payment-related messages exchanged between banks
- pain: Payment-related messages exchanged between banks and their customers
- camt: Payment advising, statements and exception handling
Within each category, specific sub-message types exist (e.g., pain.001). Below are the mappings between current message types and their ISO20022 equivalents:
| Message type mapping | |
| Current type | ISO20022 type |
| ACH credit transfer | pain.001 |
| ACH reject | pain.002 |
| ACH direct debit | pain.008 |
| ACH return | camt.053 |
| FAIM customer transfer | pacs.008 |
| FAIM bank transfer | pacs.009 |
| FAIM cover payment | pacs.009 cover |
| FAIM return message | pacs.004 |
| SWIFT MT103 | Pacs.008 |
| SWIFT MT202 | Pacs.009 (core,adv) |
| SWIFT MT202Cov | Pacs.009 (cov) |
| SWIFT MT192/MT292 | camt.056 |
| SWIFT MT196 | camt.029 |
| SWIFT MT210 | camt.057 |
| SWIFT MT900/MT910 | camt.054 |
| SWIFT MT920 | camt.060 |
| SWIFT MT940/MT950 | camt.053 |
| SWIFT MT941/MT942 | camt.052 |
The ISO20022 standard introduces new data fields that financial institutions must incorporate, including:
- ULTIMATE_CREDITOR
- ULTIMATE_DEBTOR
- INITIATING_PARTY
- REMITTANCE_INFORMATION
JP Morgan, a leading global payments provider, has published a detailed mapping guide for SWIFT messages and their ISO20022 equivalents.
Compliance challenges and solutions
Through testing ISO20022 implementation across the industry, Cygnus Compliance has identified several critical issues affecting compliance systems:
Data truncation risks
Transaction monitoring systems aligned to the current SWIFT 4 x 35 character limit require field-size adjustments. ISO20022 expands dedicated name and address fields to 105 characters. Without proper accommodation, truncation will cause partial data loss, leading to undermonitoring in transaction monitoring systems.
New field integration
The introduction of fields like ULTIMATE_CREDITOR and ULTIMATE_DEBTOR requires:
- Development of new governance policies
- Proper mapping to data elements in transaction monitoring systems
- Consideration for AML purposes
Text-based message tags
ISO20022 replaces number-based tags (e.g., [72:]) with text-based tags (e.g., [Originator]). Some sanctions filters may inadvertently screen these text-based message tags, generating high volumes of false positives.
Comprehensive coverage
Some message tags from the new ISO20022 formats may not be properly screened for sanctioned entities, particularly with new fields. As the maximum number of data points increases with ISO20022, filters have limits on screening capacity. A comprehensive field-by-field sanctions coverage test needs to be conducted.
Preparing for compliance
Financial institutions must take a systematic approach to ISO20022 implementation:
- Remap systems to the new payment format at the data element level
- Accommodate increased data volume and new fields
- Ensure effective governance and ingestion as model input
- Complete regression testing on impacted controls
Pay special attention to compliance systems (transaction monitoring, sanctions screening, customer risk rating models) to prevent data loss and under-monitoring of risk




 Kevin Lee is a managing director at Cygnus Compliance. He formerly served in a variety of roles AML RightSource, Navigant and Exiger.
Kevin Lee is a managing director at Cygnus Compliance. He formerly served in a variety of roles AML RightSource, Navigant and Exiger.